Immutable dates with proper timezone with EasyAdmin and Symfony Forms
Symfony is the best PHP framework I ever experienced.
EasyCorp/EasyAdminBundle is to me the best solution to create cool and fully customizable backends in no time.
However, something is a bit cumbersome: managing dates with timezones.
You know, when you have a legacy application that says “Event starts at this day, at this time” and you don’t know which timezone it refers to? You know when twice a year you are like forced to check the date because of daylight saving time, and calculate the timezone offset every time you have to submit a form with a date in it?
Now, forget about this issue, let’s fix it right now.
For this, we will use EasyAdmin, but in the end, it is mostly using plain old Symfony Form component.
If you already have an application using EasyAdmin, or just the Form component, you can directly go to the Timezone handling section.
Setup the project
Let’s create a sample project with the following commands:
composer create-project symfony/skeleton my_project
cd my_project
composer require --unpack admin form orm translation twig validator
composer require --unpack --dev debug maker profiler
This will be enough to set up the project with default data.
Check that you have a running database, whatever kind you want (mysql, postgresql…), and update .env accordingly if needed.
Then, we must create an entity. Let’s go for an Event class, as if we were recreating a Mobilizon-like platform:
$ bin/console make:entity Event
created: src/Entity/Event.php
created: src/Repository/EventRepository.php
Entity generated! Now let's add some fields!
You can always add more fields later manually or by re-running this command.
New property name (press <return> to stop adding fields):
> startsAt
Field type (enter ? to see all types) [datetime]:
> datetime_immutable
Can this field be null in the database (nullable) (yes/no) [no]:
>
updated: src/Entity/Event.php
Add another property? Enter the property name (or press <return> to stop adding fields):
>
Success!
Next: When you're ready, create a migration with make:migration
Some notes on this:
- A
startsAtfield only is enough for our example. In the end, we will have to do the same thing for all other date-related fields. - We will use a
DateTimeImmutableobject, because it’s important to make sure that modifications are effectively stored when the object is modified. - We do not use
datetimetz_immutablebecause I assume you will use MySQL or SQLite. But if you are using PostgreSQL, you should usedatetimetz_immutable, since it is capable of storing the timezone in a date field, contrary to other DBMS (Oracle and SQL Server 2008+ are also capable of storing timezones).)
Now that the entity is created, we can initialize the database:
bin/console doctrine:database:create
bin/console make:migration
bin/console doctrine:migration:migrate --no-interaction
All these steps are mandatory to make EasyAdmin work, nothing more.
To run the server, we will use the Symfony CLI tool, it’s probably the easiest way to set up a PHP server these days.
$ symfony serve --daemon
Stream the logs via symfony.exe server:log
[OK] Web server listening on https://127.0.0.1:8000 (PHP CGI 7.3.4)
The --daemon option will run the server in the background. In case it stops, just restart it with the same command.
Then, let’s continue.
EasyAdmin
EasyAdmin is installed but it has no configuration.
We must update it with our Event entity.
Let’s make it as straightforward as possible:
# config/packages/easy_admin.yaml
easy_admin:
entities:
Event:
class: App\Entity\Event
form:
fields:
- property: startsAt
type: datetime
Head to https://127.0.0.1:8000/admin/?action=new&entity=Event
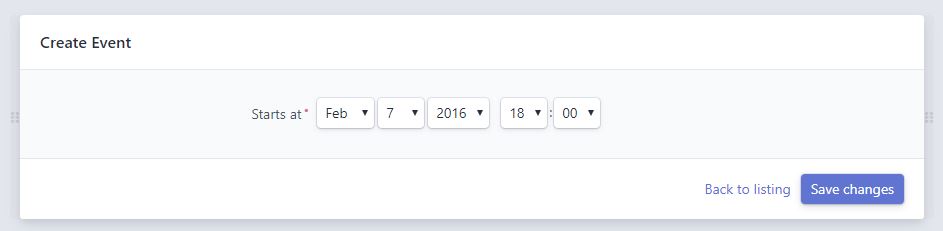
Timezone handling
With EasyAdmin, each form field can use the type_options parameter as options for the associated FormType.
By looking at the Symfony\Component\Form\Extension\Core\Type\DateTimeType class, we can see that there are two options used for handling timezones: model_timezone and view_timezone.
This is cool, because it’s not widely known and it achieves exactly what we might want to automatize: storing a unique timezone in our database, but using another one in frontend.
We’ll update EasyAdmin’s configuration:
# config/packages/easy_admin.yaml
easy_admin:
entities:
Event:
class: App\Entity\Event
form:
fields:
- property: startsAt
type: datetime
# Add these fields
type_options:
# The frontend-side timezone
view_timezone: Europe/Paris
# The timezone that will be stored in the database
model_timezone: UTC
What will this config do?
- Submit the date as if it was having
Europe/Paristimezone - Convert the submitted date to UTC
- Store the date with UTC timezone in the database.
In such case, if you submit the form with date 2016-02-07 18:00:00, with our Europe/Paris timezone, the finale object that will be persisted by EasyAdmin will look like this:
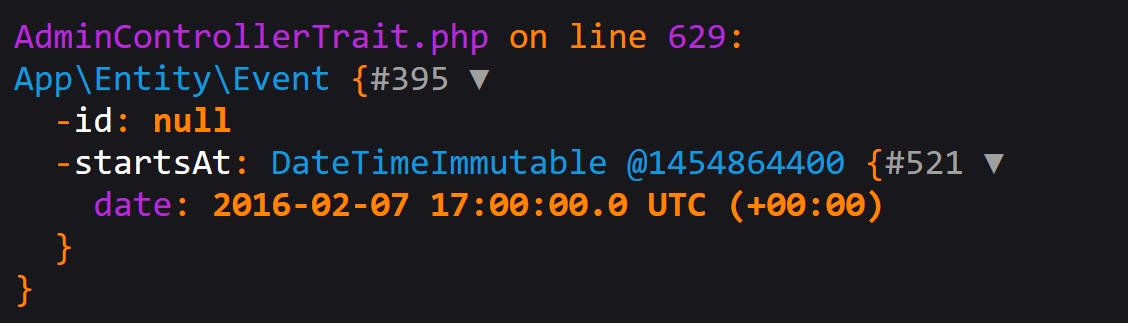
The Form component, with the help of the Data Transformers related to the DateTimeType form type, converted the date from Europe/Paris to UTC.
Conclusion
We need to remember a few things:
- We set the date to be a
datetime_immutablein the database, so we need to tell theDateTimeTypeto return us an instance ofDateTimeImmutable. For safety. - We must remember that for now this option will be hardcoded in our configuration. If you want to make it dynamic (which is a good thing!), you can do it by overriding EasyAdmin’s default controller for your entity, override the
createEntityFormBuilder()method and add the option to thestartsAtform field dynamically based on whatever data you like (HTTP headers, persisted user locale, etc.). - We must determine what timezone will be stored in our database. A good recommendation is to store everything in UTC format, and convert it frontend-side
Going forward
Next step?
Create a Form Type that combines a DateTimeType and a TimezoneType so you can configure it by yourself in the form before saving it in the database!
Try it out, and give me feedback if you do :)